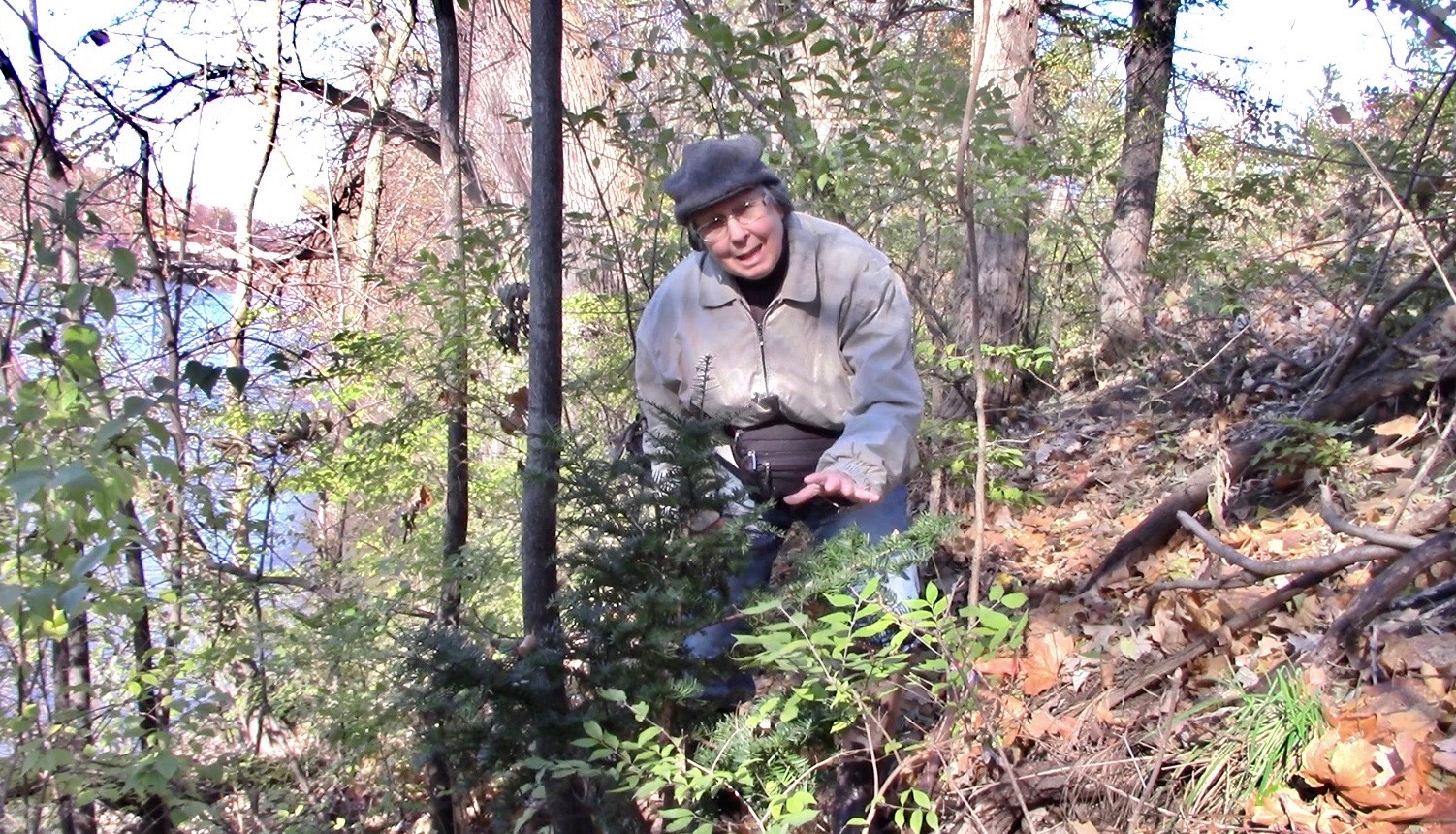
November 2021, Connie chanced upon a thrilling discovery. Although she judged the downtown, steep slopes of the Huron River to be deer-free, she had no proof. So it would still be risky to free-plant torreya seeds there. Surprisingly strong evidence appeared when she began to free-plant torreya seeds, 4 to 6 inches deep, on the high, steep slope across the river from the floodplain park. There it was: a single volunteer yew plant in perfect form, unbrowsed by deer.
 |
|
LEFT: Mid November, Connie crouches by the perfect little yew, while filming her "Helping Subcanopy Trees Migrate" video.
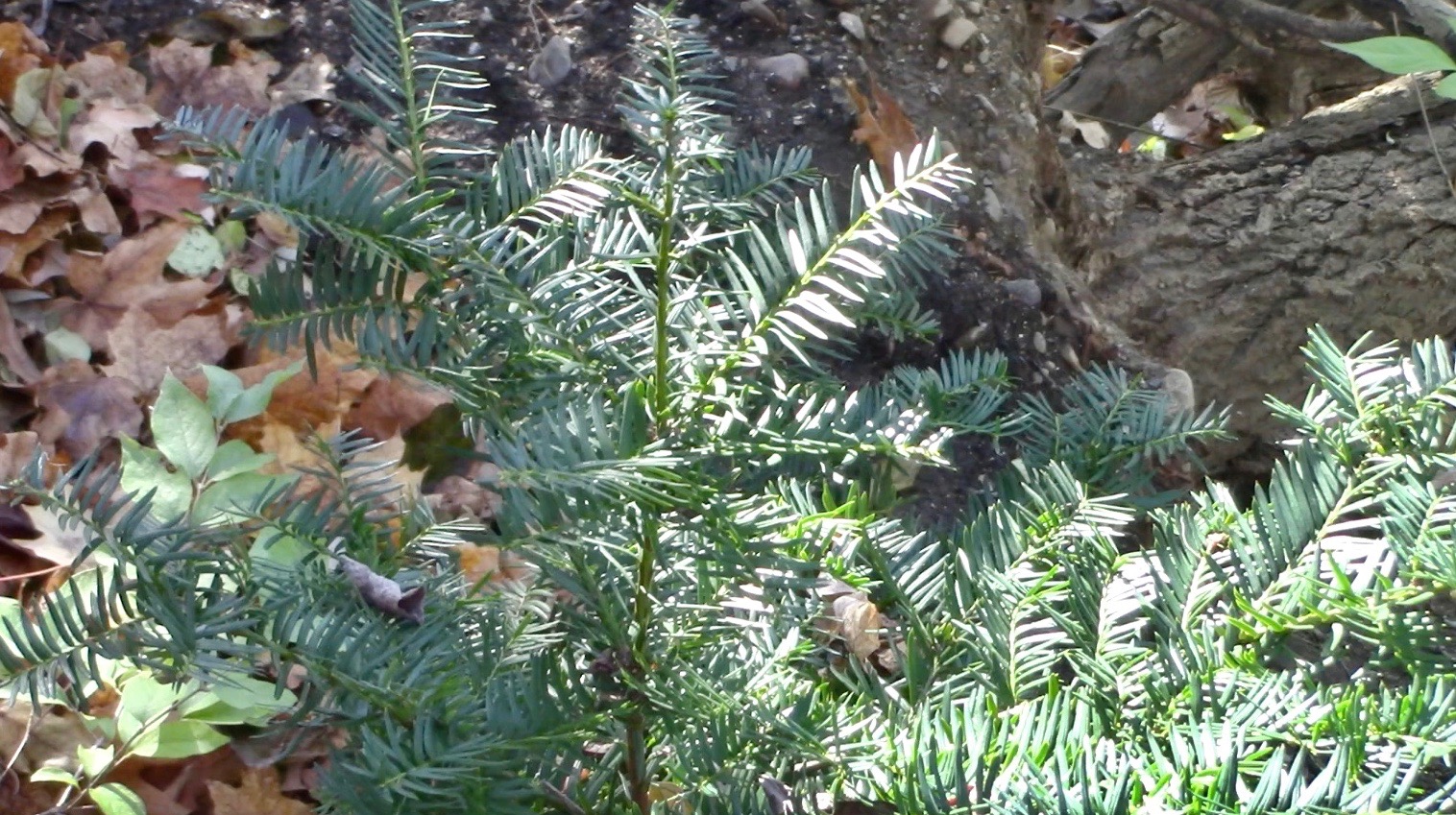
BELOW: Closeup of the yew, along with a March 2022 clear view of the yew. In November, the exotic Amur honeysuckle subcanopy shrubs still maintained their green leaves. But following winter, the only greenery left on the slope was the little yew. (Michael Dowd in the photo.)
|
 |
|  |
 |
|
My share (some 400 seeds) from this year's harvest of torreya seeds from one horticultural planting in Clinton, NC, is mostly being used at or near my home in Ypsilanti, Michigan, for experimental plantings — especially at exceedingly rare DEER-FREE SITES along our major river. (Deer herbivory has been so problematic for volunteer planters that losses have been great or investments in deer-proof cages have been necessary.)
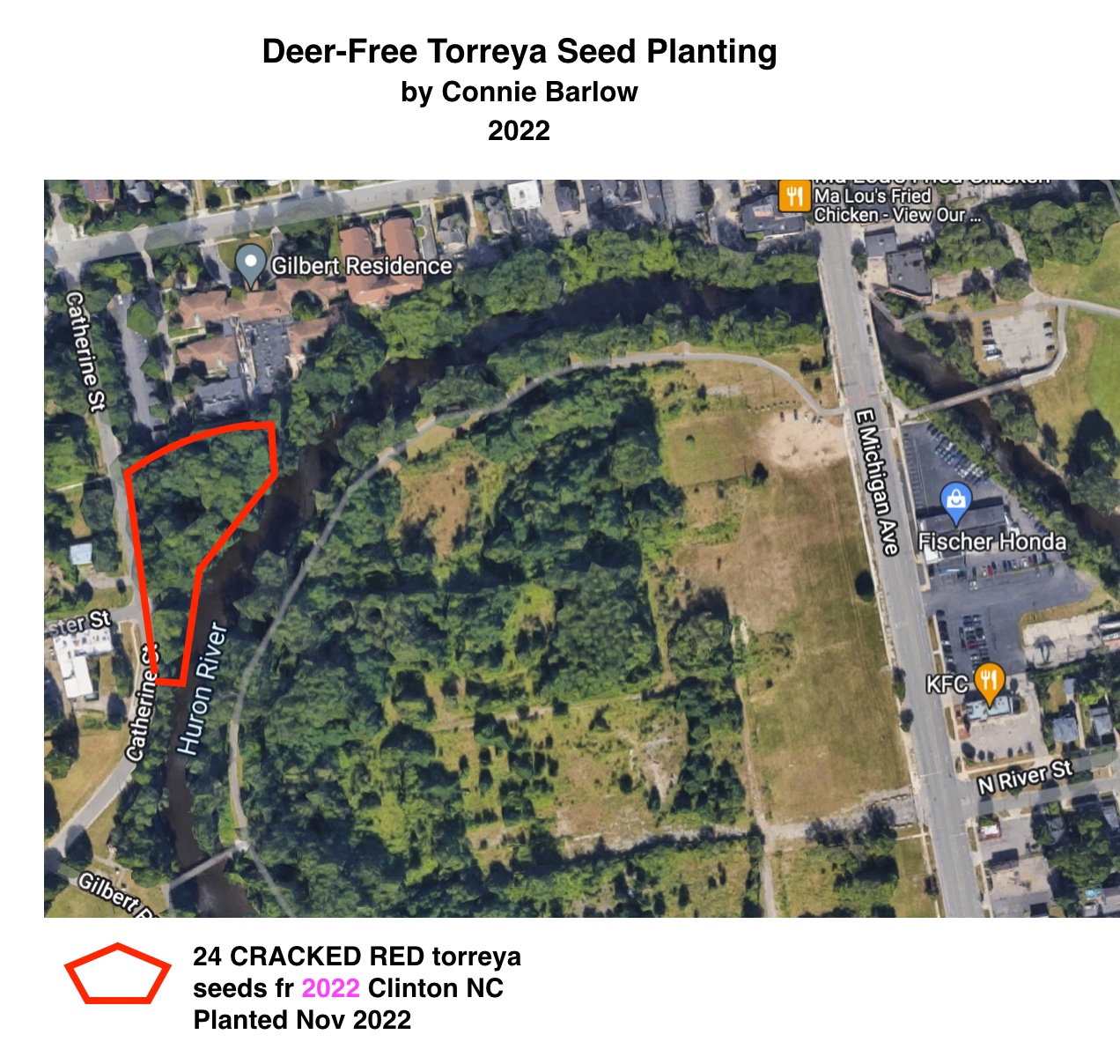
Each DEER-FREE site is located on a downtown stretch of steeply sloping forested edges of the Huron River. These were reinforced long ago by solid concrete lower portions (red outline on map above) or a series of concrete and asphalt blocks onto which trees and woody plants (especially Amur Honeysuckle) have taken hold. Natural regeneration over many decades have produced patches of good soil into which I put seeds (usually 4 to 6 inches deep, to escape detection by rodents) of America's most endangered conifer tree.
|
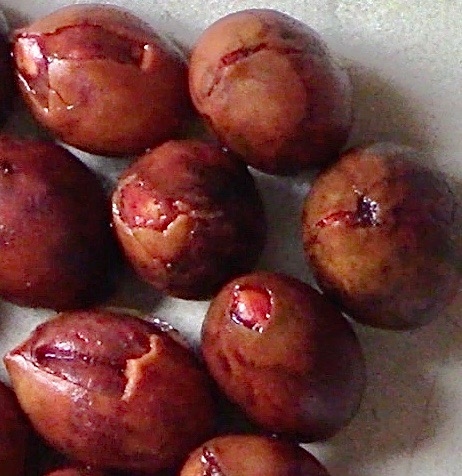
PHOTO ABOVE shows the unusual cracked seedcoats of a small portion of the 2022 harvest, through which the vibrant red seed itself is seen — clearly, not yet rotting. So these I needed to put into final destinations immediately. As well, the cracked seed farthest right displays a dark indentation on its round, non-germinating end (germination happens at the pointy end). So some of these seeds I also planted this month (turquoise outline above).
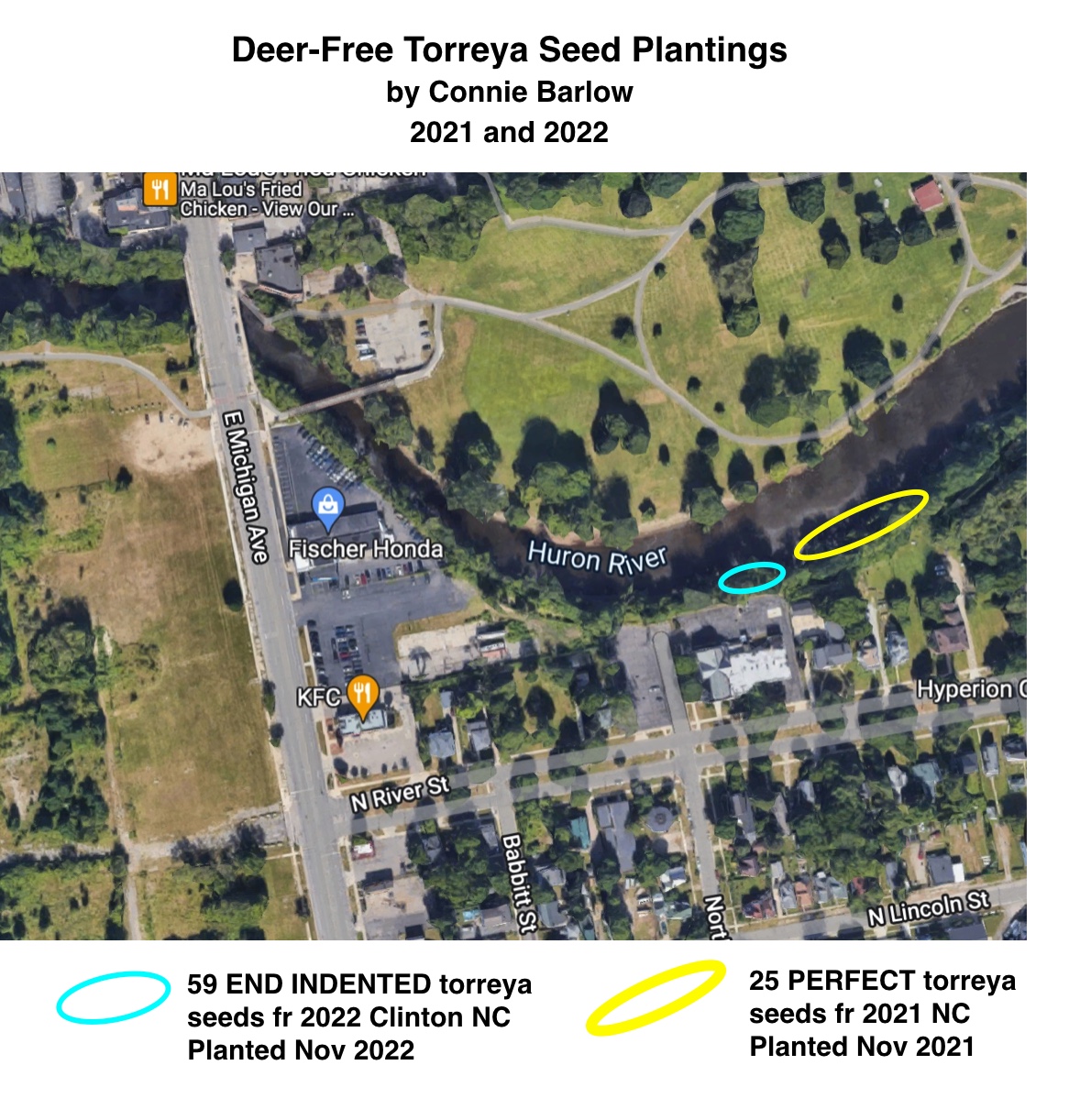
• DEER-FREE HURON RIVER SLOPE - SITE 1:
 |
|
Seed-planting began in November 2021 on the steep slope of the river across from a large floodplain city park evident in the google map image at left.
The first planting site is marked by the yellow oval.
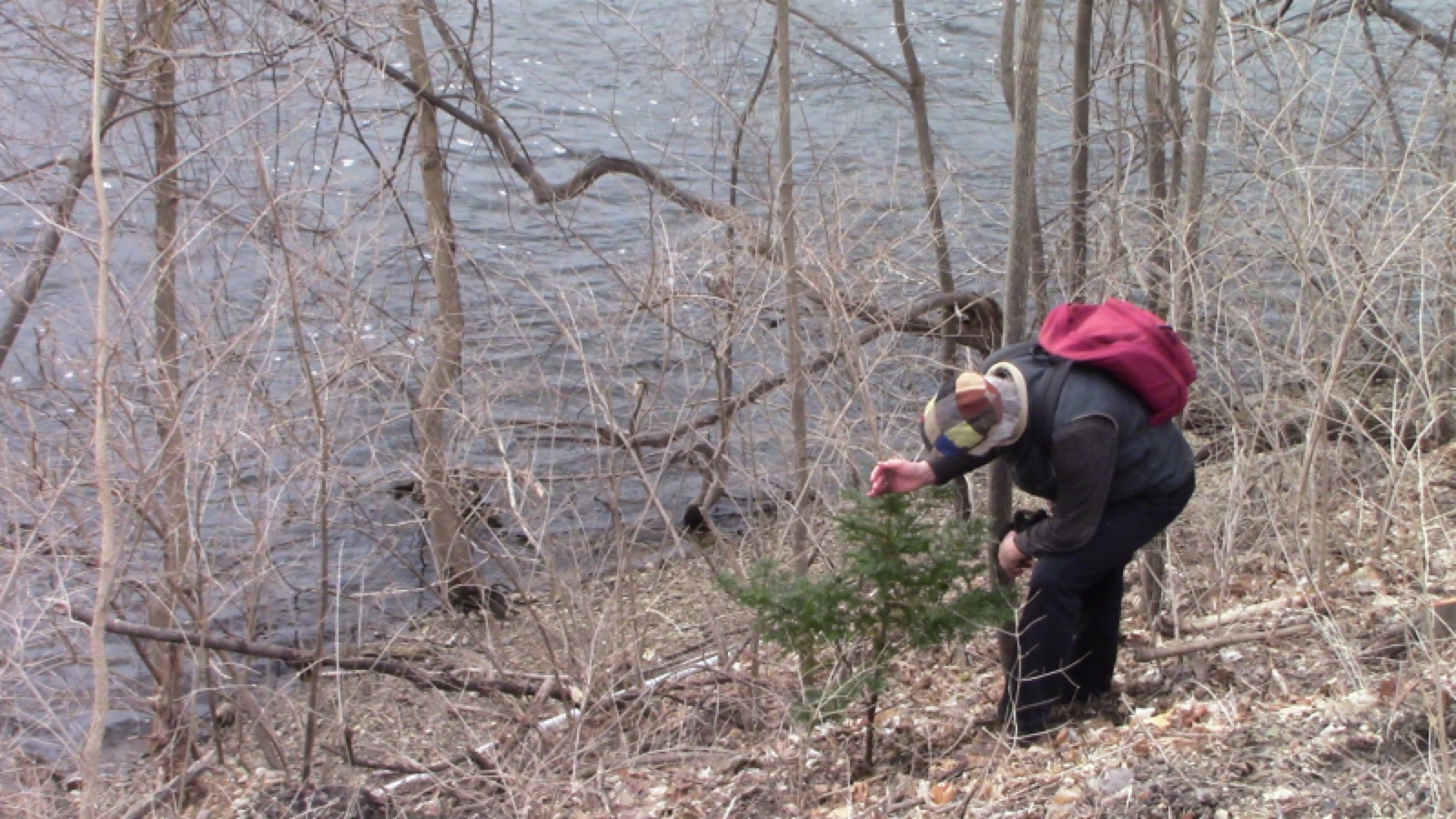
Exactly a year later, Connie planted seeds in the turquoise oval region, which was much more difficult, and for two reasons:
(1) The entire slope was very steep, and
(2) Large blocks of concrete for preventing erosion dominated the slope, so soil patches were harder to find.
--------
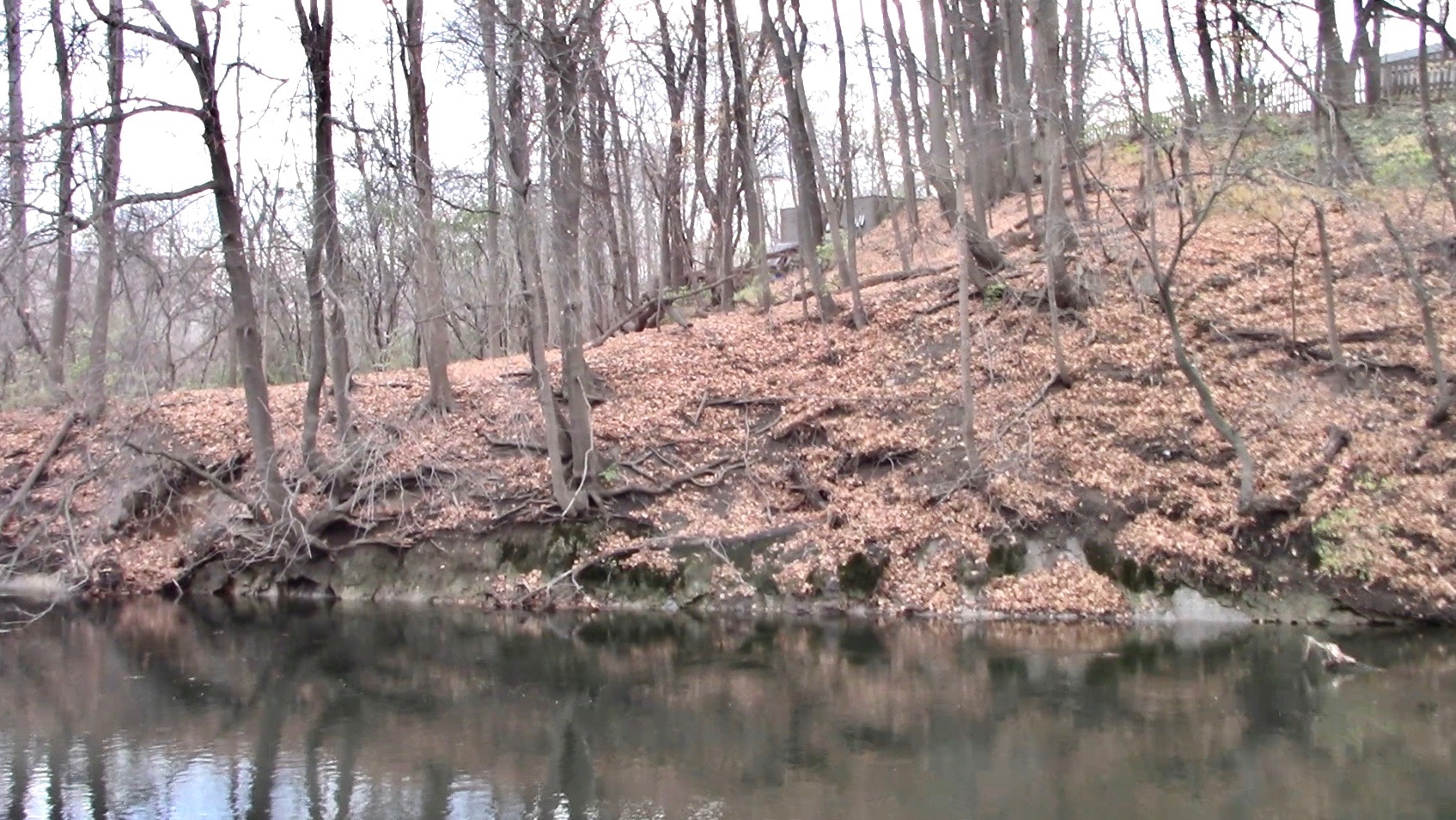
BELOW: Summer and winter scenes of the steep, forested slope (viewed from the bridge). The RED STAR marks the spot where the perfect little yew abides. A huge, leaning walnut tree on the left of the star is visible in the winter photo.
|
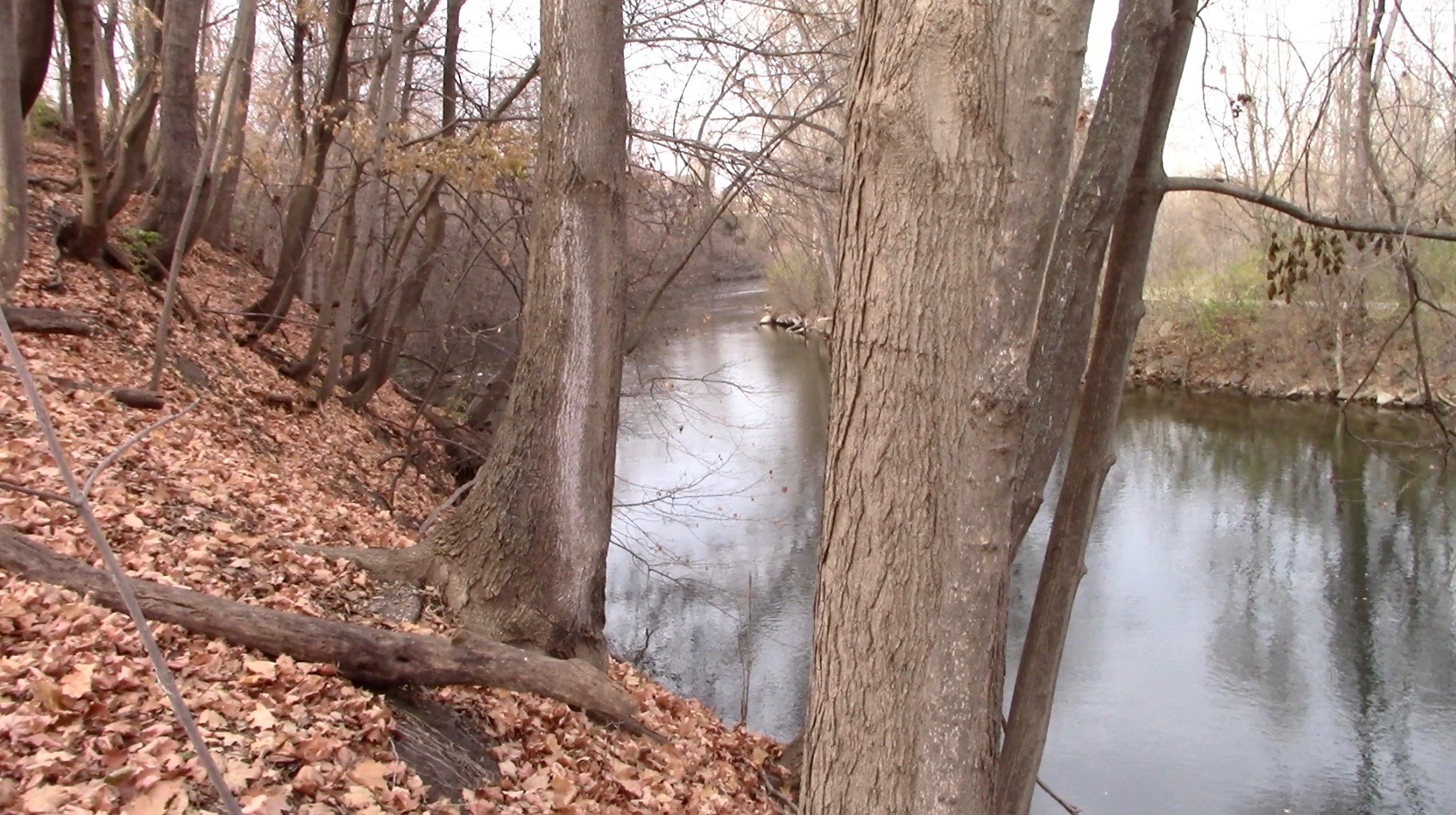
BELOW: Viewed from the floodplain park, the big walnut tree is not the only marker for where to look for the perfect little yew. A white plastic pipe is directly below the yew, which resides about halfway up the slope.
ABOVE: Seeds were planted upstream (left) of the walnut in November 2021, and downstream of the white pipe in November 2022.
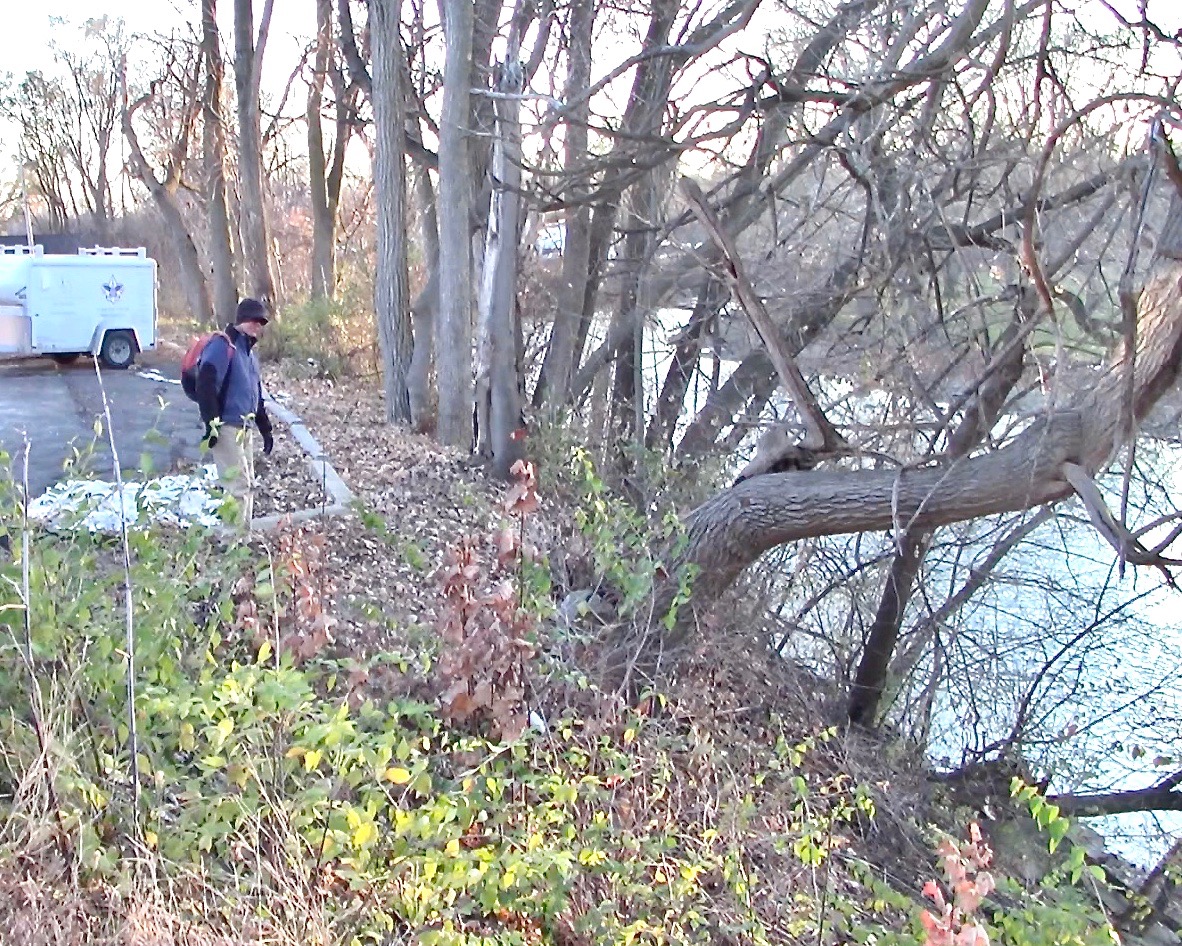
BELOW: November 2022, Michael Dowd stands at the edge of the paved parking lot of the old church: SITE 1 TURQUOISE PATCH (on the Site 1 map).
 |
|
Directly down from there is where Connie spent 90 minutes creeping and crawling along the steep slope, which was a patchwork of concrete blocks and soil patches.
There she planted 59 of the 2022 North Carolina (Clinton) seed harvest that looked perfect, except for circular, dark indentations on the round end (opposite of the pointy end) of the seeds.
This will be an experiment, in part, to discern whether such indentions impair ultimate germination or perhaps speed it up.
While planting, Connie was grateful for abundant Amur honeysuckle, which provided secure handholds on this dangerous slope.
|
• DEER-FREE HURON RIVER SLOPE - SITE 2:
 |
|
E. Michigan Ave. crosses the Huron River on this map for Site 2 as well as the map for Site 1.
The river flows from right to left on this map. The planting area for Site 2 is thus downstream of Site 1.
Here, the high bank of the river is on the opposite side.
Ypsilanti is a "rust-belt" city, and thus a large industrial area abandoned when the automobile and aircraft industry left town entails the bulk of the image. Fortunately, it is well into the process of spontaneous reforestation.
Even so, Connie engages in guerrilla rewilding only on the high slope. Here is where thick soils can be found. As well, a tall fence streetside precludes deer entry.
|
 |
 |
|
ABOVE: View of SITE 2 from the bike path on the opposite side of the Huron River and a look upstream from the site itself. The slope was too steep and too reinforced by old concrete for Connie to venture onto. But she was grateful (and surprised!) to find easy-planting acreage with good soil between the river slope and the barbed-wire fence along the street. (See below.)
ABOVE: A residential fence demarcates the end of planting possibilities. On this first planting venture, Connie did not plant farther in that direction than the fallen logs in the photo left. Lower down in the angular deer-free area was extremely good soil, populated by Amur honeysuckle beneath the deciduous canopy. Connie also planted in their midst.